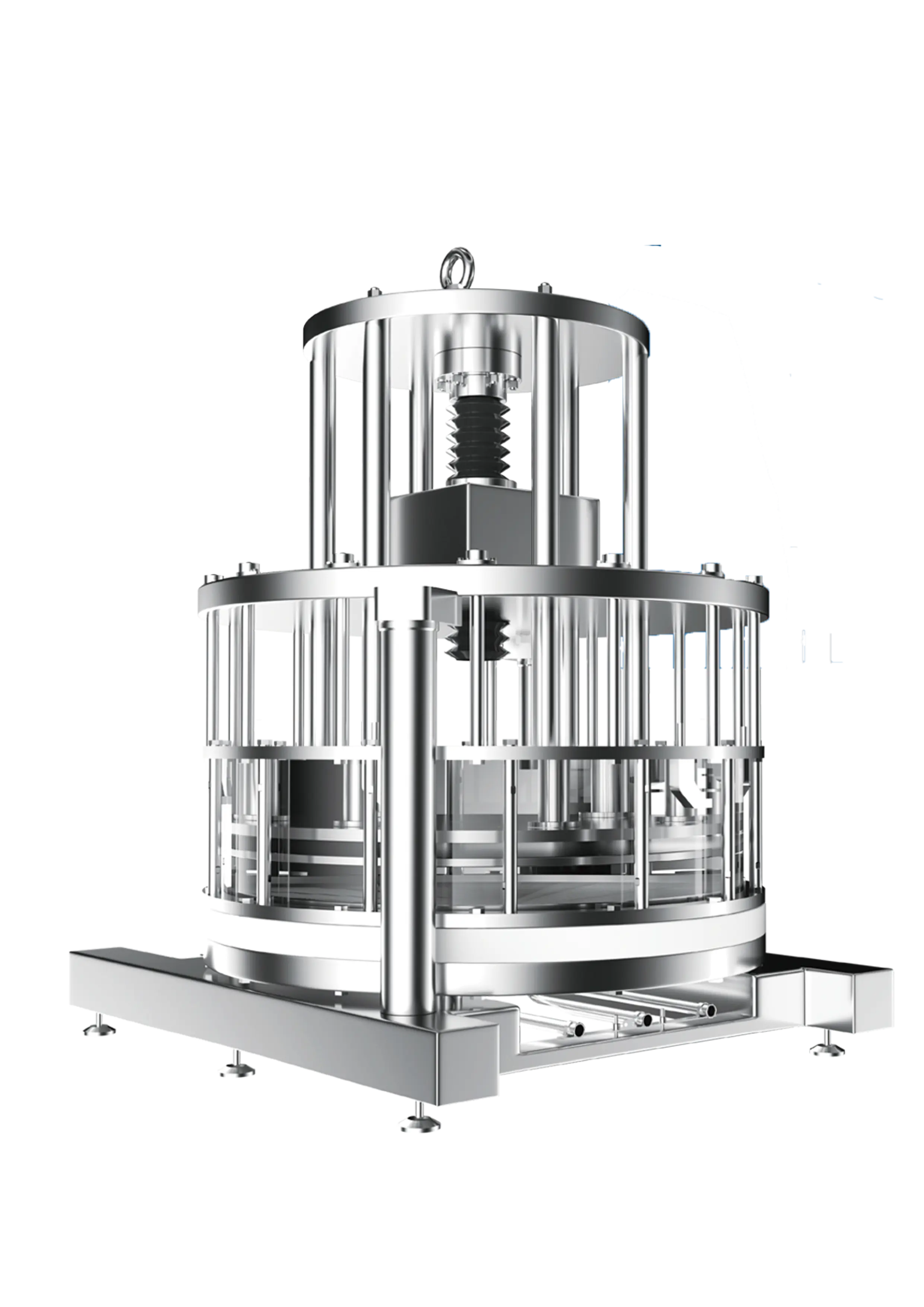


Chromatography is a widely used technique in biopharmaceutical purification. It involves the separation of molecules based on their physicochemical properties, such as charge, size, or affinity for a specific ligand. The mixture is passed through a column containing a stationary phase, and the target molecule(s) selectively bind to the stationary phase while the impurities pass through. The target molecule(s) can then be eluted from the column for further processing.