Small nucleic acid drugs represent a new generation of revolutionary therapies, following in the footsteps of small-molecule chemical drugs and antibody-based protein medications. These drugs are short-chain nucleic acids—specifically designed with unique sequences and functions—synthesized chemically. Typically composed of just a dozen to several dozen or even longer nucleotides, they don’t directly target proteins. Instead, they focus on disease-related mRNA or non-coding RNAs, disrupting the process by which genetic information is transferred from DNA to proteins to exert their therapeutic effects.
Figure 1: Inclisiran Sodium Injection
Inclisiran, a prime example of an siRNA-class drug, is an innovative lipid-lowering medication and the world’s first approved siRNA-based therapy specifically designed for lipid management. SiRNAs are artificially synthesized short double-stranded RNA molecules that achieve gene silencing by targeting specific mRNA molecules. Unlike conventional small-molecule or antibody-based therapies, siRNAs directly interfere with protein synthesis at the post-transcriptional level, classifying them as nucleic acid–based drugs. At its core, Inclisiran works by leveraging RNA interference (RNAi) technology to suppress the production of PCSK9 protein in the liver, thereby reducing levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Incliran consists of two oligonucleotide chains: the sense strand, which contains 21 nucleotides and is terminated with a GalNAc ligand for hepatocyte targeting, and the antisense strand, complementary to the sense strand. The antisense strand specifically binds to and degrades PCSK9 mRNA via the RNA interference mechanism. In the case described here, the sample—synthesized using the Bio Oligo100 laboratory-grade nucleic acid synthesizer after process optimization—was subsequently analyzed by HPLC.The sense strand crude product achieves a purity of 86.2%, while the antisense strand crude product reaches 84.4%. Additionally, the average coupling efficiency for monomers can attain up to 99%, resulting in outstanding synthesis performance.
Bio Oligo 100 is a laboratory-grade nucleic acid synthesizer capable of producing synthesis scales ranging from 50 pmol to 9 mmol. Featuring a modular design and an intelligent software system, this device can efficiently synthesize precise amounts of DNA and RNA when paired with synthetic columns of various specifications. Equipped with high-precision piston pumps and utilizing flow-through solid-phase synthesis technology, the system significantly reduces reagent consumption while enabling scalable, linear amplification.
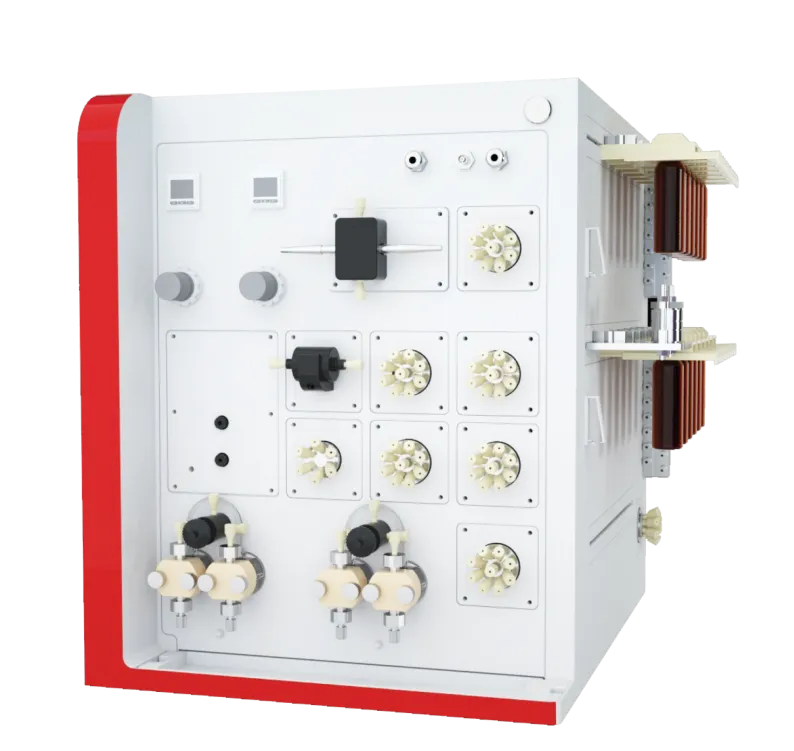

Figure 2: Bio Oligo 100 Laboratory Nucleic Acid Synthesizer
Step | Flow Rate |
Deprotection | 400 cm/h |
Deprotection Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
Coupling Injection | 2.5 + 3.75 ml/min |
Coupling | 230 cm/h |
Coupling Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
Oxidation | 3.25 ml/min |
Oxidation Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
Sulfurization | 1.39 ml/min |
Sulfurization Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
Capping | 0.5 + 0.5 cv/min |
Capping Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
DEA (Cleavage) | 75 cm/h |
Wash | 200 + 200 cm/h |
Table 1: Process Parameters for Inclisiran Synthesis on the Bio Oligo 100 System
(*Process description for a 6.3 mL synthesis column; specific parameters are programmed into the software workstation.)
Synthesis Process Monitoring:
The synthesis system utilizes a UV detector to monitor the absorption value of the DMT group during the deprotection step in real-time. After the deprotection wash step, the cleanliness of the wash is determined by the absence of a peak or the presence of a specific peak in the UV signal. Through multiple experimental observations and comparisons, the optimized method precisely controls the deprotection time and reagent usage, avoiding depurination impurities caused by prolonged deprotection time or excessive acid concentration.
The effectiveness of monomer coupling is judged by monitoring fluctuations in conductivity during the coupling step. Abnormally low conductivity may indicate insufficient monomer delivery or potential issues with pipeline sealing.
The progress of synthesis for each monomer is assessed by changes in the conductivity peak value and profile during the oxidation/sulfurization step. Furthermore, whether the conductivity drops below 0.05 mS/cm is used to determine if the oxidant has been thoroughly washed away, preventing over-oxidation due to excessive residue.
Hardware/Software Configuration:
High-precision piston pumps are used to strictly control the amount of reagents used in each step, further optimizing the monomer equivalents during the reaction process. This not only reduces raw material costs but also mitigates the risk of sequence truncation (N-1) or extension (N+1) defects from the source, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the full-length strand.
During synthesis, under software control, valves switch accurately and rapidly, ensuring synthesis precision. The user-friendly software supports both Chinese and English interfaces. Process parameters for stages not yet executed can be modified at any time during the synthesis run, facilitating observation of each monomer step and enabling real-time process optimization.
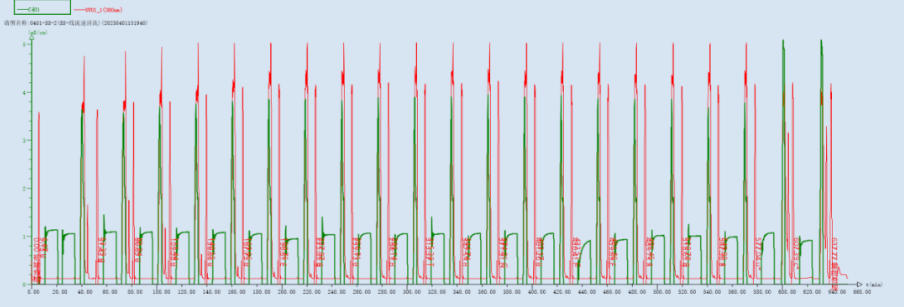
Figure 3: UV 350 nm and Conductivity Monitoring Profile During the Entire Sense Strand Synthesis Process
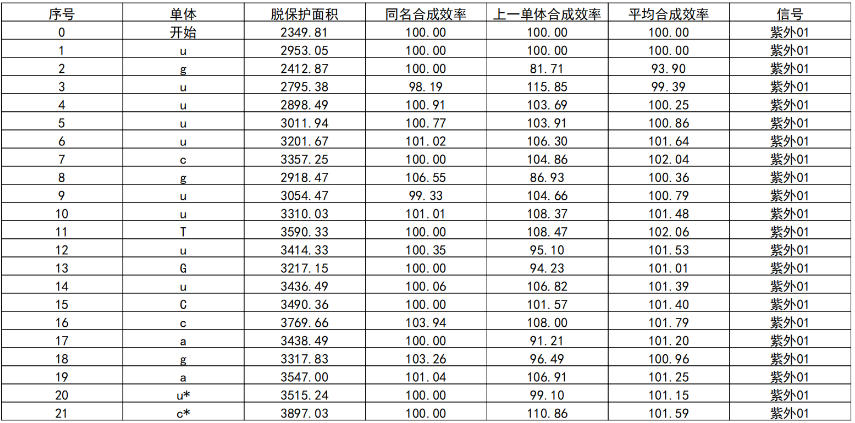
Table 2: Real-Time Monitoring of Synthesis Efficiency During Sense Strand
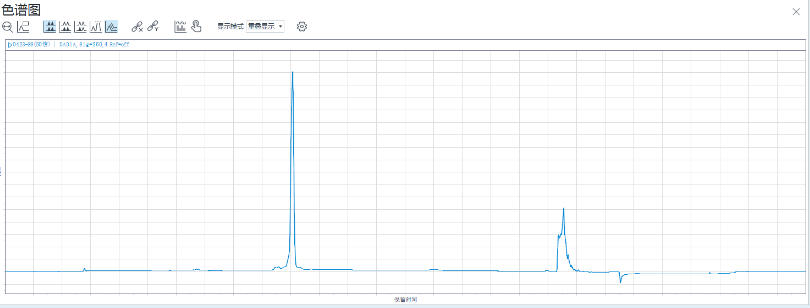
Figure 4: HPLC Analysis of the Sense Strand
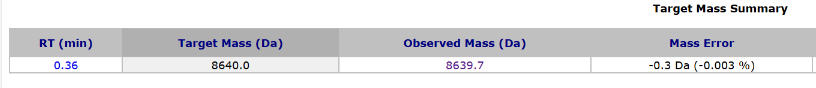
Figure 5: Mass Spectrometry Analysis of the Sense Strand
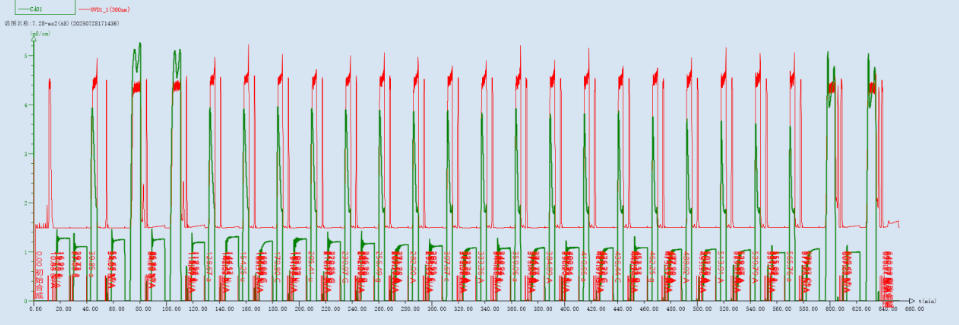
Figure 6: UV 350 nm and Conductivity Monitoring Profile During the Entire Antisense Strand Synthesis Process
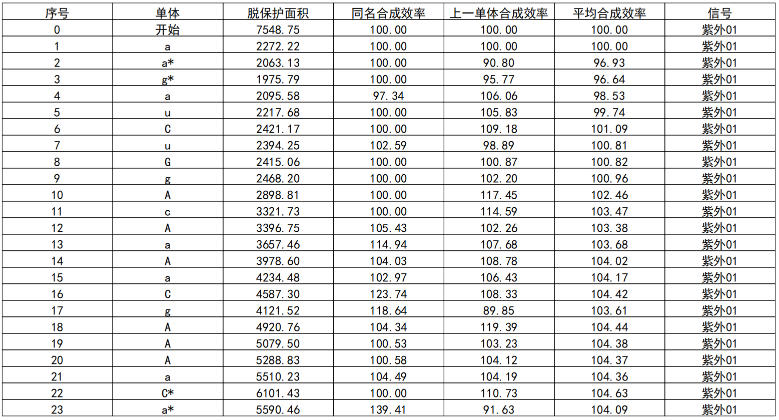
Table 3: Real-Time Monitoring of Synthesis Efficiency During Antisense Strand Synthesis
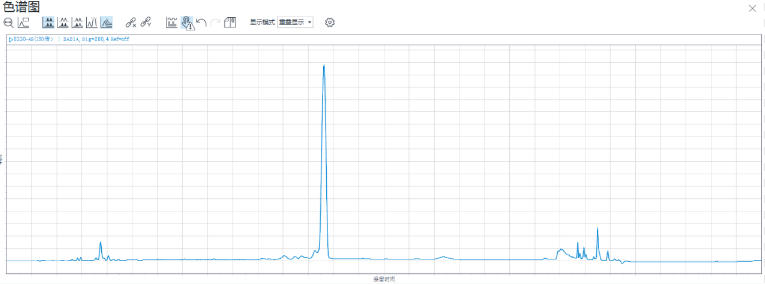
Figure 7: HPLC Analysis of the Antisense Strand

Figure 8: Mass Spectrometry Analysis of the Antisense Strand
Analysis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) showed that the crude purity of the synthesized Inclisiran sense strand was 86.2%, and the crude purity of the antisense strand was 84.4%. The average monomer coupling efficiency reached 99%, and mass spectrometry confirmed the correct molecular weight. This data indicates that, even without any purification, the target full-length sequence constitutes a high proportion of the synthesis product, with a sharp main peak and well-controlled impurities (N+, N-), laying a solid foundation for subsequent purification processes and promising a high yield of purified product.
Mass Spectrometry (MS) results confirmed that the molecular weights of the synthesis products perfectly matched the theoretical molecular weights of the Inclisiran sense and antisense strands, confirming accuracy. This fundamentally verifies the successful synthesis of the intended nucleic acid sequences, with all chemical modifications correctly incorporated and no unintended modifications or degradation occurring.
The above case study, completed using the Bio Oligo 100 laboratory nucleic acid synthesizer, validates the instrument's efficient, rapid, and reliable performance in oligonucleotide synthesis. The excellent crude product purity highlights the outstanding synthesis efficiency, operational stability of the Bio Oligo 100 system, and the convenience of method optimization offered by the new software version. The synthesizer's software supports both Chinese and English interfaces, allows customizable protocol writing, offers strong user autonomy, and automatically calculates theoretical reagent consumption and tracks real-time usage based on the synthesis process, aiding in thorough pre-synthesis preparation. Hanbon Sci & Tech's Bio Oligo 100 nucleic acid synthesizer can also meet users' personalized customization needs and is suitable for oligonucleotide synthesis applications of different scales and types.
Hanbon Sci. & Tech's Overall Solution for Nucleic Acid Drugs
Hanbon Sci. & Tech. Co.,Ltd. provides customers with a complete product portfolio encompassing nucleic acid synthesis systems, chromatography systems, preparative HPLC systems, and tangential flow filtration(TFF) systems, offering comprehensive support from basic research and process development to scaled production. The company's product line meets the full range of needs from laboratory-scale exploration and pilot process scale-up to industrial-scale production. With stable and reliable system performance and flexible, scalable configuration options, Hanbon provides solid technical support and solutions for the entire workflow of nucleic acid therapeutics, from early R&D to commercial manufacturing.

Figure 9: Integrated Solution for Nucleic Acid Drug Production